Maintaining a well-balanced diet is vital during pregnancy, but even the healthiest diet can sometimes fall short in delivering all the nutrients required for your baby’s growth. This is where prenatal multivitamins play an essential role, ensuring that both the mother and baby get the critical nutrients they need.
1. Why Take Prenatal Vitamins?
Prenatal multivitamins are designed specifically for pregnant women to fill nutritional gaps in their diet. Even if you maintain a healthy, varied diet, certain nutrients can be hard to obtain in adequate amounts. For instance, women who are vegetarian, vegan, lactose intolerant, or have severe morning sickness often struggle to meet the nutrient requirements for pregnancy.
Taking prenatal vitamins from the moment you find out you’re pregnant (or even earlier if you’re planning to conceive) helps ensure that your body has enough reserves of essential nutrients like folic acid and iron.
2. Key Nutrients in Prenatal Vitamins
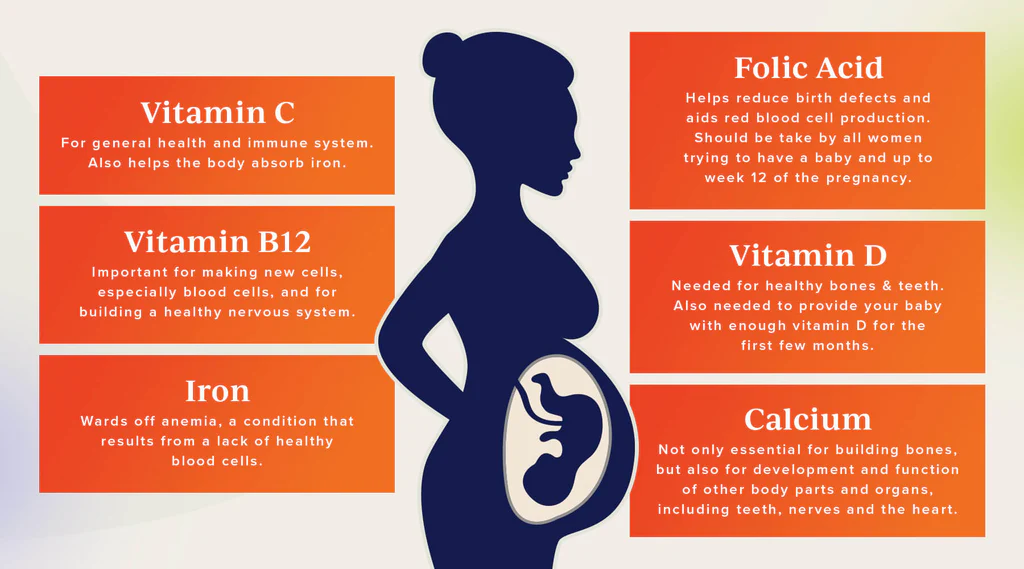
There are several key nutrients that every prenatal vitamin should contain. Each one plays a vital role in your pregnancy:
Folic Acid
Folic acid is one of the most important components of prenatal vitamins. It helps prevent neural tube defects in your baby, affecting the brain and spinal cord. Expecting mothers need at least 400-600 micrograms of folic acid daily to ensure proper development during the early stages of pregnancy.
Iron
Iron is crucial for producing the extra blood your body needs to carry oxygen to your baby. Pregnant women are more prone to anemia due to increased blood volume, and iron deficiency can cause fatigue or even preterm birth. Prenatal vitamins typically provide around 27-30 milligrams of iron to meet these needs.
Calcium
Calcium is necessary for building strong bones and teeth for your baby. If you don’t get enough calcium from your diet, your body will take it from your bones, which can weaken your own bone health. Most prenatal vitamins provide around 1,000 milligrams of calcium, though supplements may be recommended in some cases.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) is an omega-3 fatty acid crucial for your baby’s brain and eye development. Not all prenatal vitamins include DHA, so women who do not consume enough fish may need to take an additional omega-3 supplement.
3. Timing and Dosage
Ideally, you should start taking prenatal vitamins before conception. Neural tube development happens within the first month of pregnancy, so having sufficient folic acid is critical. Continue taking prenatal vitamins throughout the pregnancy and even while breastfeeding, as your body continues to need extra nutrients to support your baby’s growth.
4. Troubleshooting Common Side Effects
Prenatal vitamins can cause mild side effects such as nausea, constipation, or an upset stomach. If you experience these, try taking the vitamins with a light snack or before bedtime. Increasing fiber intake and drinking plenty of water can also help relieve constipation. If your symptoms persist, consult your healthcare provider for alternatives, such as a different formula or chewable vitamins.
Conclusion
Prenatal multivitamins and minerals are an essential part of a healthy pregnancy. By ensuring that you receive key nutrients like folic acid, iron, and calcium, these supplements can help support your baby’s development and maintain your health. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any supplements to ensure they meet your individual needs.